Key Concepts and Terms
To help you get started in InEight Estimate, you should know a few key terms:
-
Job Folder
-
Library
-
Form
-
Cost Item
-
Pay Item
-
Resource
-
Assembly
Job Folder
Job folders hold all the information for an individual project estimate. It is possible to import master data into a job folder, but when you work in a job folder it is independent, meaning any activity performed in that folder will not affect any other jobs and will not affect the library.
When moving back and forth between jobs, make sure to always double-check that you are in the right job.
Library
The Library is a storehouse for master data, such as:
• Labor, equipment, and material unit cost rates
• Standard account codes
• Units of measure
When you create a new job from scratch, default data and settings copy from the Library into your new job folder, except for the resource rates. Multiple list of resource rates can be maintained in the library so you must select which rates to populate a new estimate with. Four tag fields are available to filter the resource rates you bring into an estimate from the master library. For example, you may select a subset of your labor rates based on the geographical location of the project.
Form
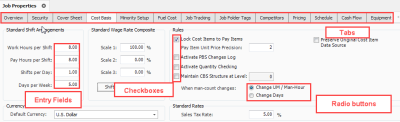
Any screen you open in InEight Estimate is considered a Form. There are three types of forms: Standard, Register, and Record forms.
Standard Forms resemble typical data entry forms with fields available to fill in key project information. They also may contain radio buttons or checkboxes to define settings for the job.
InEight Estimate uses tabs to group and organize entry fields and settings in a logical way, so that the information is easy to access.
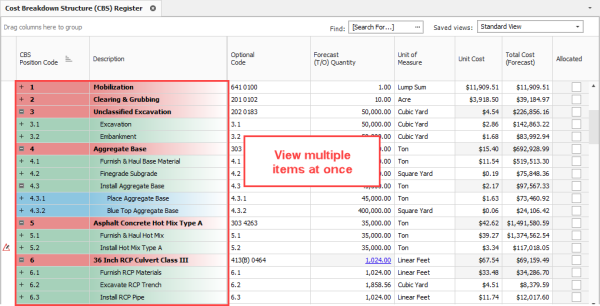
Register Forms have a grid format of rows and columns, giving it a spreadsheet look and feel. Register forms allow you to see information for multiple items at once. The Cost Breakdown Structure (CBS) Register is an example of a register form.
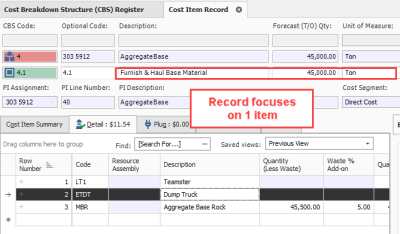
In a register form, you can open a Record for individual items you want to drill into.
The Tab key is the best way to move among fields in InEight Estimate (instead of the Enter key).
The below figure displays a Cost Item Record accessed by double clicking on that item on the Cost Breakdown Structure (CBS) Register.
Cost Item
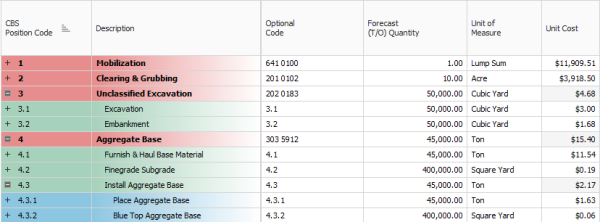
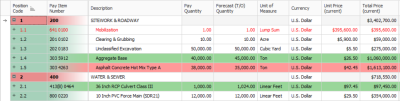
Cost items are the individual cost-related activities that make up the project. Cost items are organized into a hierarchy in the Cost Breakdown Structure (CBS) Register. Each row in the CBS is considered a cost item.
Pay Item
Pay items typically represent the owner required deliverables a contractor must submit pricing for. Pay items are used to distribute the cost calculated in the Cost Breakdown Structure, with all markup, including any fees or contingencies calculated in the Price Breakdown Structure. This allows the total estimate value to be distributed to a structure that is different than the CBS. Pay Items are predominantly used by contractors to prepare a bid sheet. Owners may use pay items to identify funding sources or for various reporting needs.
Resource
Resources are the building blocks of a detailed cost estimate.
Resources are the people, equipment, material, and supplies needed to complete the project. Resources are employed to cost items to develop an estimate, and are organized into seven categories or types:
-
Labor
-
Construction Equipment
-
Rented Construction Equipment
-
Installed Equipment
-
Installed Materials
-
Supplies
-
Unique
Resource Assembly
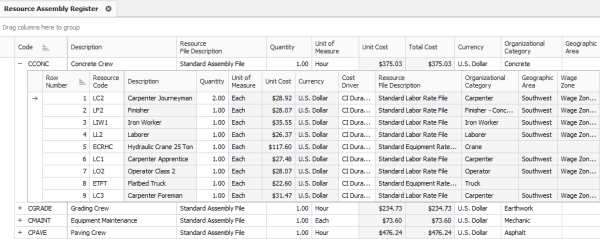
A Resource Assembly is a group of resources that are often used together. For example, for civil work, you may group together an operator foreman, operator, and laborer, along with a loader and excavator. When estimating, you can employ this assembly which includes all of the pre-selected resources.
Cost Item Assembly
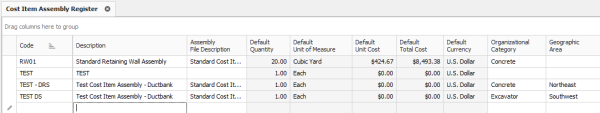
A Cost Item Assembly is a predefined group of cost items that has cost based on estimator inputs to a set of questions. Cost item assemblies provide parameter-driven estimating and can also refer to reference tables. They allow companies to create intelligent construction systems to automatically estimate various scopes of work, based upon a user providing specification and dimension variables.